RBI’s new credit reporting rules could impact your credit score! Learn how late payments, loans, and credit card usage will be tracked. Discover tips to improve your CIBIL score and secure faster loan approvals under the revised norms. Stay informed to protect your financial health!
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has introduced change in the financial sector with its revised credit reporting rule, effective from January 1, 2025. This policy mandates lenders to update credit bureau records every 15 days, a significant shift from the earlier monthly reporting cycle. This reform aims to enhance the accuracy and timeliness of credit information, directly impacting how credit scores are calculated and managed. For Indian borrowers, this regulation promises faster reflection of financial behaviour, potentially reshaping access to loans, interest rates, and overall financial health. In this comprehensive blog post, we explore the intricacies of the RBI’s new credit reporting rule, its implications for your credit score, the ideal credit score to aim for, and actionable steps to leverage this change for better financial outcomes.
Understanding the RBI’s New Credit Reporting Rule
The RBI’s directive, announced in August 2024, requires all lenders, including banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), to submit credit information to Credit Information Companies (CICs) such as CIBIL, Experian, Equifax, and CRIF High Mark every 15 days. Previously, credit bureaus relied on monthly updates, which often led to delays in reflecting borrowers’ repayment behavior. For instance, timely loan repayments or defaults could take up to 40 days to appear on a credit report, potentially misrepresenting a borrower’s creditworthiness. The new 15-day cycle, effective from January 1, 2025, ensures that credit reports are updated on the 15th and last day of each month, with data submission required within five calendar days.
This policy aligns with the RBI’s broader goal of fostering transparency, accuracy, and fairness in the credit ecosystem. By mandating fortnightly updates, the RBI aims to empower borrowers with real-time insights into their credit profiles while enabling lenders to make informed decisions based on current data. The transition period allowed lenders and CICs to upgrade their systems, ensuring compliance with the Credit Information Companies (Regulation) Act, 2005 (CICRA). Non-compliance could result in penalties, underscoring the RBI’s commitment to enforcing this reform.
Key Features of the New Rule
- Fortnightly Updates: Lenders must report credit data every 15 days, ensuring credit scores reflect recent financial activities.
- Faster Data Processing: CICs are required to ingest data within five days of receipt, minimizing delays in score updates.
- Consumer Notification: Lenders must inform customers via SMS or email when their credit reports are accessed or if they are reported as defaulters.
- Grievance Redressal: CICs must resolve complaints within 30 days, with penalties of ₹100 per day for delays beyond this period.
- Prevention of Evergreening: The rule curbs the practice of taking new loans to repay old ones, reducing the risk of debt traps.
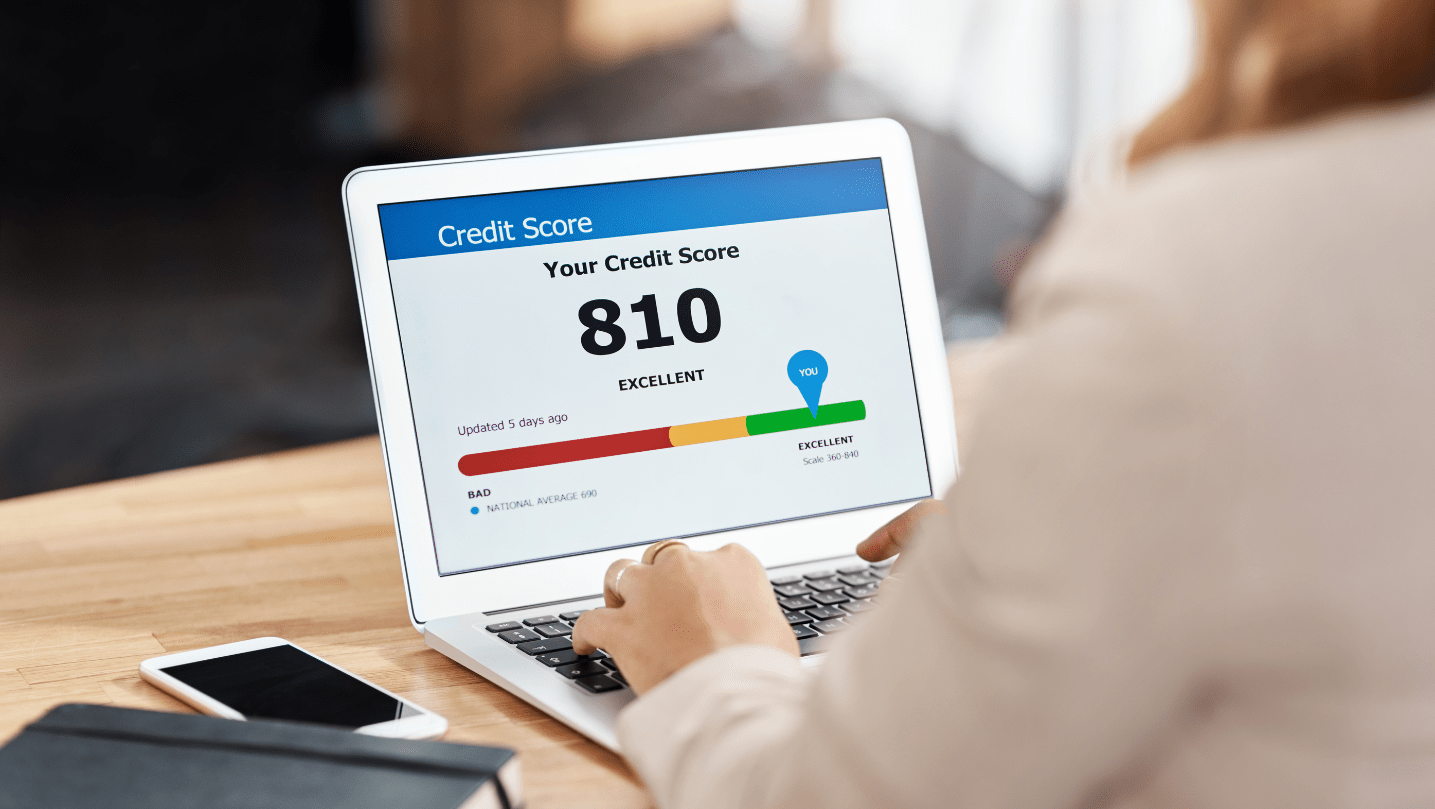
What Is the Ideal Credit Score?
In India, credit scores range from 300 to 900, with higher scores indicating better creditworthiness. The ideal credit score is generally considered to be 750 or above, particularly for CIBIL scores, which are widely used by lenders. A score in this range demonstrates a strong history of timely repayments, responsible credit utilization, and a balanced credit mix, making you an attractive candidate for loans and credit cards with favorable terms.
Why Aim for a Score of 750+?
- Easier Loan Approvals: Lenders view scores above 750 as low-risk, increasing your chances of securing personal loans, home loans, or credit cards.
- Lower Interest Rates: A high credit score often qualifies you for lower interest rates, reducing the overall cost of borrowing. For instance, a home loan applicant with a 750+ score might secure a rate of 8.5% compared to 9.5% for a score below 700.
- Higher Credit Limits: Credit card issuers are more likely to offer higher limits to individuals with strong credit scores.
- Faster Processing: Applications from high-score borrowers are often processed quickly, as lenders perceive lower risk.
Credit Score Ranges in India
- 750–900: Excellent (Ideal range for best loan terms)
- 700–749: Good (Eligible for most loans, but interest rates may be slightly higher)
- 650–699: Fair (May face higher interest rates or stricter terms)
- 300–649: Poor (Difficulty securing credit; may require collateral or guarantors)
Achieving and maintaining an ideal credit score requires consistent financial discipline, especially under the RBI’s new 15-day reporting rule, which accelerates how quickly your actions impact your score.
How the New Rule Impacts Your Credit Score
Your credit score is a critical indicator of your creditworthiness, influencing your ability to secure loans, credit cards, and favorable interest rates. The RBI’s 15-day credit reporting rule directly affects how quickly your financial behavior is reflected in your credit score. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its impact:
1. Faster Reflection of Positive Financial Behavior
Under the previous monthly reporting system, timely loan repayments or credit card bill settlements could take weeks to improve your credit score. For example, if you cleared a loan in early January, the update might not appear until February, delaying your ability to access better loan terms. With the new 15-day cycle, positive actions—such as paying off a loan or reducing credit card utilization—are reflected within two weeks. This allows disciplined borrowers to see quicker improvements in their credit scores, helping them reach or maintain the ideal 750+ range.
Example: Suppose you pay off a ₹5 lakh personal loan on January 5, 2025. Under the old system, this might not reflect until February. Now, the update will appear by January 15, potentially boosting your CIBIL score closer to the ideal 750+ and improving your chances of securing a home loan with a lower interest rate.
2. Swift Detection of Negative Behavior
Just as positive actions are reflected faster, so are negative ones. Late payments, defaults, or high credit utilization will appear on your credit report within 15 days, potentially lowering your score below the ideal range. Lenders must notify customers before reporting them as defaulters, giving you a chance to rectify issues promptly to protect your score.
Tip: Set up auto-debit for EMIs and credit card payments to avoid missing due dates, as defaults will now be reported faster and could push your score below 750.
3. Improved Access to Credit
The fortnightly updates ensure that your credit report is a more accurate representation of your financial health. For borrowers who consistently make on-time payments, this translates to faster access to credit, especially if their score is in the ideal 750+ range. Lenders can rely on up-to-date data to assess creditworthiness, reducing the risk of rejecting eligible applicants due to outdated information. This is particularly beneficial for first-time borrowers or those rebuilding their credit after past defaults.
4. Curbing Evergreening and Over-Leveraging
The RBI’s rule aims to halt “evergreening,” a practice where borrowers take new loans to repay existing ones, creating unsustainable debt cycles. With more frequent reporting, lenders can monitor borrowing behavior in real-time, identifying high-risk borrowers who apply for multiple loans simultaneously. This enhances financial discipline and reduces the likelihood of loan defaults, helping borrowers maintain scores closer to the ideal range.
5. Enhanced Transparency and Consumer Empowerment
The new rule mandates that lenders inform customers when their credit reports are accessed, increasing transparency. Additionally, borrowers can access one free credit report annually from each CIC, allowing them to monitor their credit health and report discrepancies promptly. If errors are found, CICs are required to resolve complaints within 30 days, ensuring accountability. These measures empower consumers to take control of their financial profiles and work toward achieving an ideal credit score.
Benefits for Borrowers and Lenders
The RBI’s credit reporting reform offers significant advantages for both borrowers and lenders, fostering a healthier credit ecosystem.
For Borrowers
- Quicker Credit Score Improvements: Timely payments and loan repayments boost your score faster, helping you reach the ideal 750+ range.
- Better Loan Terms: Accurate and updated credit reports increase your chances of securing loans at competitive interest rates, especially with a high score.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Frequent updates allow you to track your credit health closely and address issues promptly.
- Protection Against Errors: Mandatory notifications and grievance redressal mechanisms ensure errors in credit reports are corrected swiftly.
For Lenders
- Improved Risk Assessment: Access to recent data enables lenders to make informed decisions, reducing the risk of bad loans.
- Reduced Defaults: Real-time monitoring of borrower behavior helps identify high-risk applicants early.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Faster data processing streamlines loan application evaluations, improving operational efficiency.
- Compliance with Regulations: Adhering to the RBI’s guidelines ensures lenders avoid penalties under CICRA.
Challenges and Considerations
While the new rule is a step toward a more transparent credit system, it comes with challenges:
- Increased Monitoring for Borrowers: With faster reporting, borrowers must be vigilant about timely payments to maintain an ideal credit score.
- System Upgrades for Lenders: Smaller banks and NBFCs may face technical and operational challenges in adapting to the 15-day cycle.
- Potential for Temporary Score Volatility: Frequent updates may lead to short-term fluctuations in credit scores, especially for those with irregular payment patterns.
To address these challenges, borrowers should monitor their credit reports regularly, while lenders must invest in robust data management systems to ensure compliance.
Actionable Steps to Achieve and Maintain an Ideal Credit Score
To make the most of the RBI’s revised credit reporting rule and aim for an ideal credit score of 750+, consider these practical tips:
- Check Your Credit Report Regularly
Use your free annual credit report from CIBIL, Experian, or other CICs to monitor your score and identify errors. With updates every 15 days, checking your report bi-monthly is advisable. Report discrepancies immediately to the CIC for resolution within 30 days. - Pay EMIs and Bills on Time
Timely payments are critical, as defaults will now impact your score faster. Set reminders or enable auto-debit to ensure you never miss a due date, protecting your score from dipping below the ideal range. - Maintain Low Credit Utilization
Keep your credit card utilization below 30% of your limit. High utilization can lower your score, and with frequent updates, this will be reflected quickly. Low utilization is key to maintaining a 750+ score. - Avoid Multiple Loan Applications
Applying for multiple loans simultaneously can trigger hard inquiries, lowering your score. Space out applications and compare loan offers carefully to safeguard your credit profile. - Monitor Notifications from Lenders
Stay alert for SMS or email notifications about credit report access or default warnings. Address issues promptly to prevent negative reporting that could push your score below 750. - Refinance High-Interest Loans
If you’ve achieved an ideal credit score, explore refinancing options to secure lower interest rates, especially with the RBI’s recent repo rate cut to 6% in April 2025. - Diversify Your Credit Mix
A balanced mix of secured (e.g., home loans) and unsecured (e.g., credit cards) credit can positively impact your score. However, avoid over-leveraging, as it could lead to defaults. - Educate Yourself on Credit Management
Understand factors affecting your credit score, such as repayment history (35%), credit utilization (30%), credit age (15%), credit mix (10%), and inquiries (10%). Resources like Moneycontrol and TransUnion CIBIL offer guides to help you navigate the credit landscape.
The Broader Impact on India’s Financial Ecosystem
The RBI’s 15-day credit reporting rule is part of a broader effort to strengthen India’s financial system. By promoting transparency and accountability, the policy supports the RBI’s goal of reducing non-performing assets (NPAs) and fostering responsible lending. The rule also complements other recent reforms, such as the public repository for digital lending apps and tightened regulations on auto-debit payments, aimed at enhancing consumer protection.
For India’s growing middle class, this reform could democratize access to credit, enabling more individuals to achieve financial goals like homeownership or entrepreneurship with an ideal credit score. As the financial ecosystem adapts, the policy is expected to build a culture of financial discipline, benefiting both borrowers and lenders in the long run.
Final Thought
The RBI’s revised credit reporting rule, effective January 1, 2025, marks a significant step toward a more transparent and efficient credit system in India. By mandating fortnightly updates, the RBI ensures that credit scores reflect borrowers’ financial behavior in near real-time, empowering consumers and enabling lenders to make better decisions. Aiming for an ideal credit score of 750 or above is crucial for securing favorable loan terms and achieving financial goals. While the rule presents challenges, such as the need for increased financial discipline, its benefits—faster score improvements, better loan access, and enhanced transparency—far outweigh the drawbacks.
To thrive under this new regime, borrowers must prioritize timely payments, monitor their credit reports, and manage credit utilization effectively. By staying proactive, you can leverage the RBI’s reform to achieve and maintain an ideal credit score, unlocking better financial opportunities.
-

The Supabase India Ban Explained: Who’s Affected, Why It Happened, and What Comes Next
-

Geopolitical Shock: Bitcoin Tumbles Under $64K Following US-Israel Military Strike on Iran
-
New EPFO Rule 2026: You Can Now Withdraw 100% of Your PF Balance Without Resigning — Here’s How
-

Is Your Money Safe in Fino Payments Bank After CEO Rishi Gupta’s Shocking Arrest?