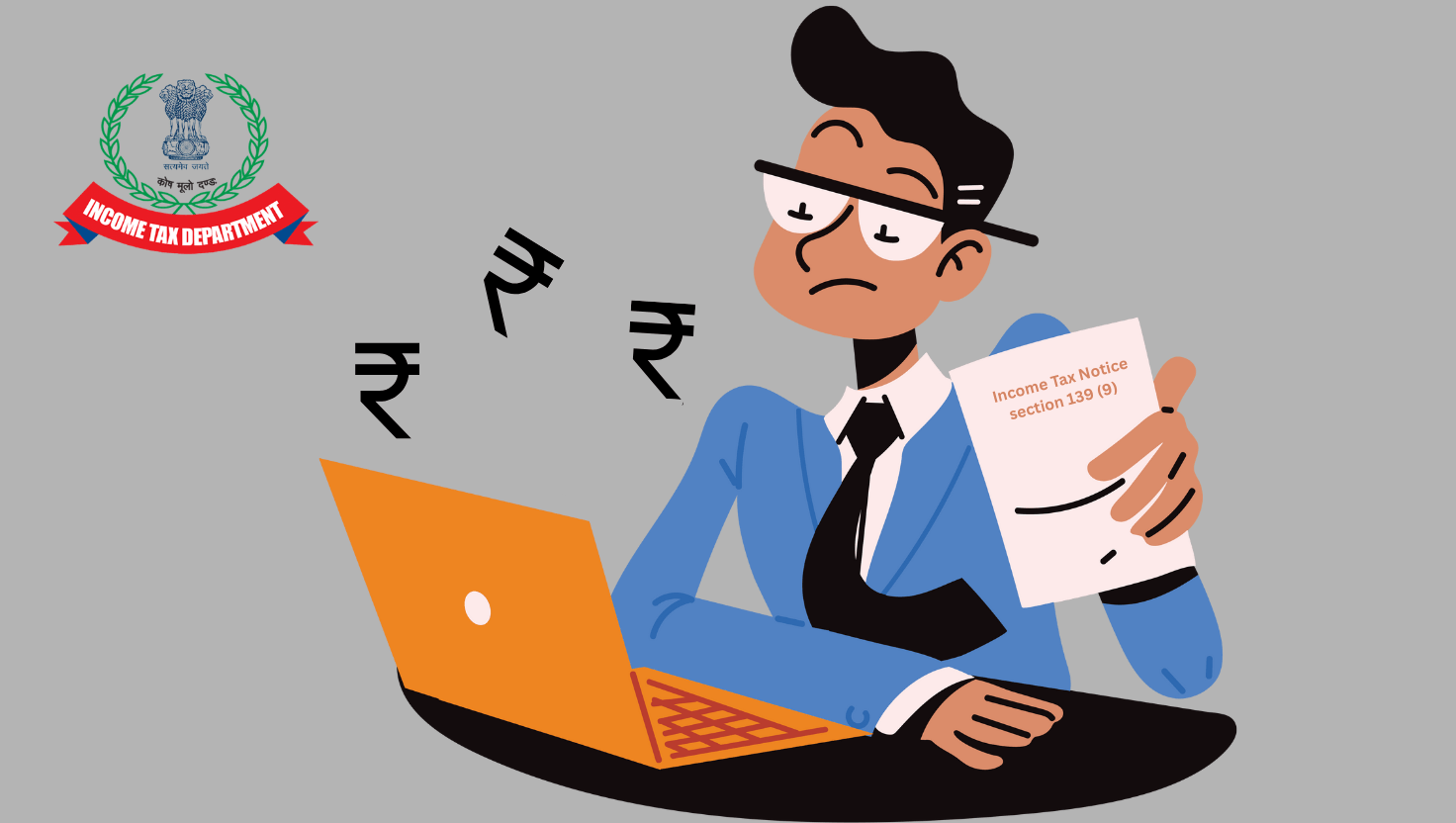
Filing your ITR perfectly, only to receive a chilling Section 139(9) Defective Return Notice! What went wrong? Could it be a crypto oversight or a TDS mismatch? In 2025, with Finance Act 2024 updates, ignoring this notice risks penalties up to Rs 5,000 or an invalid ITR.
Filing your Income Tax Return (ITR) with care, only to receive a cryptic email from the Income Tax Department. Your heart races. Is it a penalty? An audit? Or something worse? This is the reality for thousands of taxpayers in India facing a Defective Return Notice under Section 139(9) of the Income Tax Act, 1961. What triggers this notice? How can you resolve it before it’s too late? As we step into 2025, with updates from the Finance Act 2024, understanding this provision is vital to avoid pitfalls and ensure compliance in India’s evolving tax landscape. Let’s unravel the suspense behind Section 139(9), exploring its intricacies, common triggers, and actionable solutions.
What is Section 139(9) of the Income Tax Act?
Section 139(9) empowers the Assessing Officer (AO) to flag an ITR as defective if it contains errors or lacks critical details. Enacted under the Income Tax Act, 1961, this section ensures the integrity of tax filings. A defective return isn’t rejected outright; instead, the AO issues a notice, offering a window to rectify the issues. But here’s the catch: ignore the notice, and your ITR becomes invalid, as if it was never filed.
This provision applies to all taxpayers—individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), firms, and companies. For Assessment Year (AY) 2025-26, extended filing deadlines to September 15, 2025, due to Budget 2024 changes, make vigilance crucial. Notices typically arrive via email or the e-filing portal, pinpointing specific defects. Curious about what triggers these notices?
Why Does the Income Tax Department Issue Defective Return Notices?
What makes an ITR defective under Section 139(9)? The reasons often hide in plain sight, lurking in everyday oversights. Here are the most common culprits:
- Incomplete Information: Missing or incorrect PAN, mismatched names, or omitted income sources like interest from savings accounts.
- Tax Calculation Errors: Claiming Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) credits without matching income declarations.
- Bookkeeping Blunders: Failing to submit Profit and Loss accounts or Balance Sheets for businesses exceeding turnover limits (e.g., Rs 2 crore for audits).
- Wrong ITR Form: Using ITR-1 for simple incomes when you have capital gains or business income.
- Crypto and VDA Oversights: Non-reporting of Virtual Digital Asset (VDA) transactions, a growing concern in 2025.
- Exemption Discrepancies: Incorrect House Rent Allowance (HRA) claims or unreported foreign assets, especially for Non-Resident Indians (NRIs).
These errors trigger notices, but the suspense lies in how they’re detected and what happens if ignored. Let’s explore the latest data to understand the scale of this issue.
Latest Data on Defective ITR Notices in India (2024-2025)
The numbers tell a gripping story. In FY 2024-25, the Income Tax Department admitted to errors in issuing defective notices under Section 44AD (presumptive taxation), affecting thousands who filed unnecessary revised returns. Platforms like ClearTax, serving over 1.5 million happy customers, report that 20-30% of first-time filers face delays due to mismatches in Annual Information Statement (AIS) or Form 26AS.
For AY 2025-26, extended deadlines reflect systemic updates, with ITR utilities for forms like ITR-2 and ITR-3 delayed until June 2024. TaxBuddy statistics reveal that 15-20% of defective notices stem from presumptive taxation errors. YouTube tutorials on rectification saw a surge in 2024, signaling widespread issues. The Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) notes that validation rules for ITR-1 categorize defects into types A, B, and C, either preventing uploads or triggering notices. This data sets the stage for understanding common defects.
Common Defects Leading to Section 139(9) Notices
Let’s uncover the specific errors that invite scrutiny:
- Incorrect Personal Details: A typo in your email, mobile number, or PAN disrupts communication.
- Income Mismatches: Reporting salary but omitting interest income or capital gains.
- Business Oversights: Exceeding Rs 2 crore turnover without audited books or failing to file under Section 44AD/44ADA.
- Deduction Errors: Claiming Section 80C deductions without proofs or misapplying the new tax regime under Section 115BAC.
- Foreign Income Oversights: NRIs failing to report global assets or income in Schedule FA/FI.
- Tax Payment Discrepancies: Unpaid self-assessment tax or mismatches between Form 26AS and ITR.
These defects are avoidable, but the clock ticks once a notice arrives. How do you respond? Let’s break it down.
How to Rectify a Defective Return Under Section 139(9)
You have 15 days from receiving the notice to act, or face dire consequences. Here’s how to rectify:
- Log into the e-filing portal: Navigate to e-File > Income Tax Returns > File Income Tax Return.
- Select the correct option: Choose In response to notice under Section 139(9).
- Rectify errors: Download the ITR utility, correct defects (e.g., add missed income, fix calculations), and generate a new JSON/XML file.
- Upload and e-verify: Submit the rectified file and verify via Aadhaar OTP, net banking, or EVC within 30 days.
- Seek professional help: For complex cases, consult a Chartered Accountant (CA).
For updated returns (u/s 139(8A)), follow a similar process. The Income Tax India YouTube channel offers video guides for navigation. But what if you miss the deadline? The stakes are high.
Step-by-Step Guide to Responding Online
Here’s a clear roadmap to resolve the suspense:
- Check the notice: Review details on the e-filing portal or email for defect specifics.
- Gather documents: Collect Form 16, 26AS, AIS, and other proofs.
- Download ITR utility: Use the latest version (updated for AY 2025-26).
- Correct errors: Address issues like missing income or incorrect deductions.
- Generate and upload: Create a new JSON/XML file, upload under Section 139(9).
- E-verify: Complete verification within 30 days to validate the ITR.
Missed steps? The consequences are severe. Let’s explore what happens if you ignore the notice.
Consequences of Ignoring a Defective Return Notice
Ignoring a Section 139(9) notice is a costly mistake. The outcomes are chilling:
- Invalid ITR: Your return is deemed as never filed, nullifying all claims.
- Penalties under Section 234F: Up to Rs 5,000 for late filing.
- Interest under 234A/B/C: 1% per month on unpaid taxes.
- Loss of benefits: No carry-forward of losses or deductions under Sections 80C, 80D, etc.
- Scrutiny or audits: Persistent errors may trigger notices under Section 143(2).
- Prosecution risk: In extreme cases, non-compliance invites legal action.
For AY 2025-26, with extended deadlines, non-response could delay refunds or escalate penalties. Real-life cases highlight the urgency.
Real-Life Case Studies: Lessons from Defective Notices
Consider these scenarios:
- Mumbai Professional: A salaried employee received a notice for mismatched TDS. He rectified within 10 days, avoiding penalties.
- Freelancer’s Folly: A Bengaluru freelancer ignored a notice, faced a Rs 10,000 fine and interest under Section 234A.
- Erroneous Notices: In 2024, faulty Section 44AD notices led to unnecessary revisions, wasting time.
- Business Owner’s Blunder: A Delhi entrepreneur with unaudited books under Section 44AD faced ITR invalidation, re-filing belatedly.
These stories emphasize the need for prompt action. How can you avoid these traps in 2025?
Tips to Avoid Defective Return Notices
Prevention is better than cure. Follow these strategies:
- Choose the right ITR form: Use ITR-1 for incomes up to Rs 50 lakh; opt for ITR-3/4 for businesses.
- Reconcile data: Match filings with Form 26AS and AIS before submission.
- Provide proofs: Submit Form 10-IA for 80DD claims or rent receipts for HRA.
- New regime caution: Opt out of Section 115BAC if deductions are beneficial.
- Update details: Ensure accurate email, mobile, and bank details.
- Use updated utilities: Download Excel/JSON utilities for ITR-3/4, updated per Finance Act 2025.
- E-verify promptly: Complete verification within 30 days to avoid invalidation.
First-time filers should double-check bank details and income sources to sidestep common errors.
Final Thought: Empower Yourself Against Defective Notices
The suspense surrounding a Defective Return Notice under Section 139(9) need not be a nightmare. It’s a chance to perfect your ITR and stay compliant. With extended deadlines for AY 2025-26 and digital tools like the e-filing portal, taxpayers are better equipped than ever. Act swiftly, verify accurately, and consult professionals if needed. In 2025, turn the tide on defective notices and file with confidence.
Disclaimer: The use of any third-party business logos in this content is for informational purposes only and does not imply endorsement or affiliation. All logos are the property of their respective owners, and their use complies with fair use guidelines. For official information, refer to the respective company’s website.