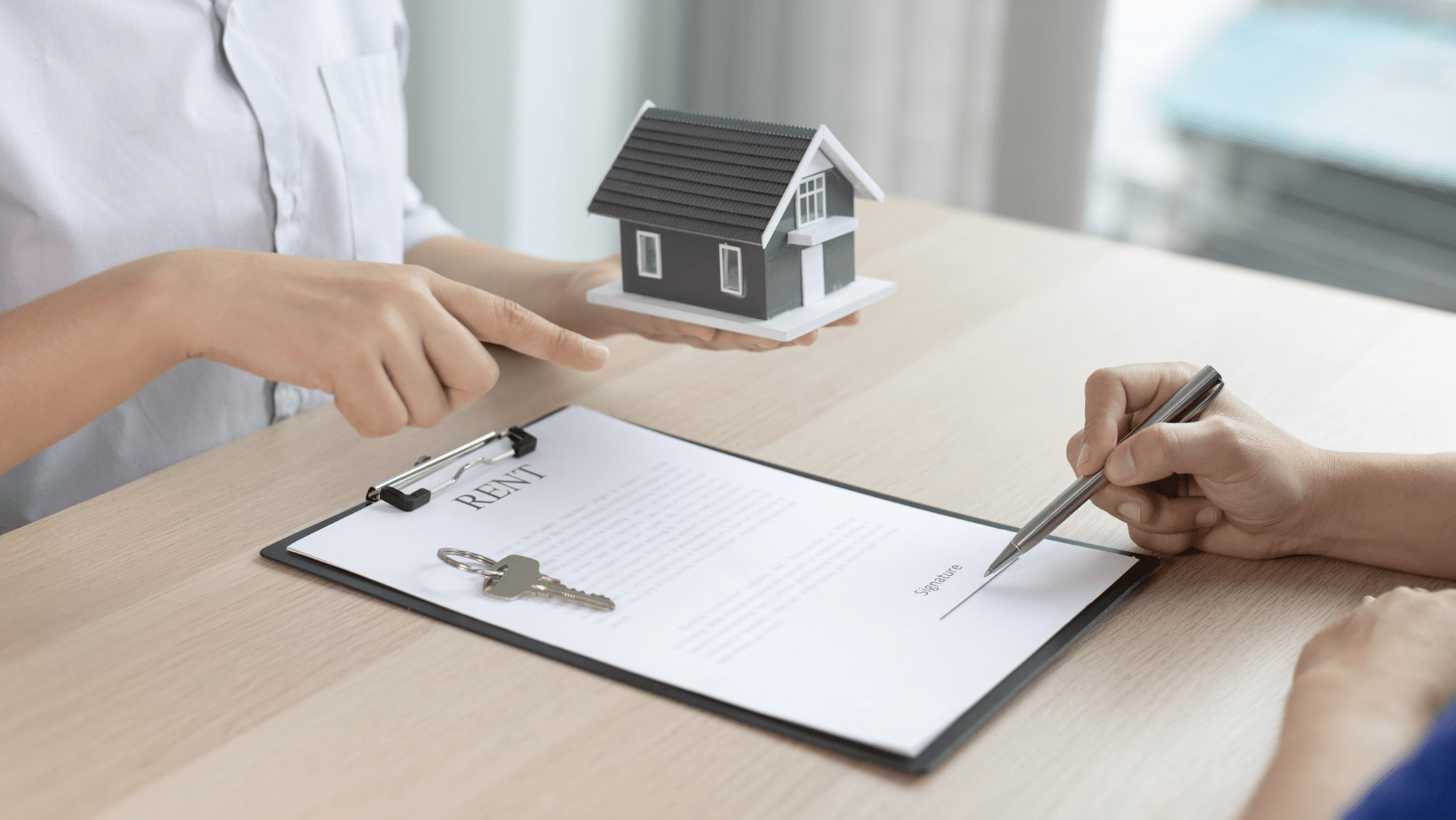
” Learn how rent payments and receipts impact your tax liability in 2025. Discover tax deductions for tenants and landlords, recent tax law changes, and tips to reduce tax burdens. Stay compliant and save with expert insights on rental income, receipts, and tax strategies. Perfect for renters and property owners! “
Understanding how rent payments and receipts impact your tax liability is crucial for both tenants and landlords. This comprehensive guide will delve into the latest tax laws, providing you with the information you need to navigate this complex area. We’ll cover key aspects such as deductible expenses, taxable income, and the importance of maintaining accurate records.
Tax laws can be intricate, especially when it comes to rent payments and receipts. Whether you’re a landlord or a tenant, knowing how these transactions affect your tax liability can save you money and prevent legal issues. This blog post will break down the essential elements of rent-related tax laws, offering insights and practical advice.
Understanding Rent Payments and Receipts
Rental income is a significant source of revenue for millions of individuals and businesses worldwide. However, it also comes with tax obligations that vary depending on your role in the rental transaction. For landlords, rental income is taxable, while tenants may be eligible for deductions under specific circumstances. Understanding how rent payments and receipts factor into your tax liability is essential for staying compliant with the law and minimizing your tax burden.
According to the IRS, rental income includes any payment received for the use or occupation of property. This includes not only monthly rent but also advance rent, security deposits (if not returned), and any expenses paid by the tenant on behalf of the landlord.
The Role of Rent Receipts in Tax Compliance
Rent receipts are more than just proof of payment—they play a critical role in tax compliance for both tenants and landlords.
a. Why Rent Receipts Matter
- For Tenants: Rent receipts can serve as proof of residency and may be required to claim deductions or credits.
- For Landlords: Rent receipts help track rental income and expenses, making it easier to file accurate tax returns.
b. How to Maintain Proper Documentation
- Use digital tools or software to generate and store rent receipts.
- Ensure receipts include details such as the date, amount paid, property address, and names of the tenant and landlord.
- Keep records for at least three years, as the IRS may audit returns within this period.
Deductible Expenses for Landlords
Landlords can deduct a wide range of expenses associated with their rental property. These deductions can help lower your tax liability and improve your overall financial situation. Here are some common deductible expenses:
- Mortgage Interest: If you have a mortgage on your rental property, the interest you pay is deductible.
- Property Taxes: Property taxes paid on your rental property are also deductible.
- Repairs and Maintenance: Costs incurred for repairs and maintenance are deductible, but improvements must be depreciated over time.
- Insurance Premiums: Premiums for insurance policies related to your rental property are deductible.
- Utilities: If you pay for utilities on behalf of your tenants, these costs are deductible.
- Depreciation: You can depreciate the cost of your rental property over its useful life, providing a significant tax benefit.
Record-Keeping and Documentation
Maintaining accurate records is essential for both tenants and landlords. Proper documentation ensures that you can substantiate your claims and deductions in case of an audit. Here are some tips for effective record-keeping:
- Keep Receipts: Save all receipts related to rent payments and expenses.
- Use Accounting Software: Consider using accounting software to track income and expenses.
- Maintain a Logbook: Keep a logbook of all transactions, including dates, amounts, and descriptions.
- Store Documents Safely: Store your records in a safe place, either physically or digitally.
Tax Implications of Rent Receipts
Tax Implications for Tenants
While tenants are not directly taxed on rent payments, there are scenarios where rent can impact their tax liability:
a. Rent as a Deduction
In some cases, tenants may be able to deduct rent payments from their taxable income. For example:
- Home Office Deduction: If you use part of your rented home exclusively for business purposes, you may be able to deduct a portion of your rent as a business expense.
- State-Specific Programs: Certain states offer rent relief or tax credits for low-income tenants. For instance, California’s Renters’ Tax Credit provides a credit of up to $120 for qualified renters.
b. Reporting Rent Assistance
If you receive government assistance to pay rent (e.g., Section 8 housing), this is generally not considered taxable income. However, it’s essential to report any such assistance accurately on your tax return.
Tax Implications for Landlords
Landlords have more significant tax obligations when it comes to rental income. Here’s what you need to know:
a. Declaring Rental Income
All rental income must be reported on your tax return. This includes:
- Monthly rent payments
- Advance rent
- Non-refundable security deposits
- Payments for canceling a lease
b. Deductible Expenses for Landlords
The good news is that landlords can deduct various expenses associated with renting out a property. These include:
- Mortgage Interest: Interest paid on loans used to acquire or improve the rental property.
- Property Taxes: State and local taxes on the rental property.
- Maintenance and Repairs: Costs for keeping the property in good condition.
- Utilities: If paid by the landlord.
- Insurance: Premiums for landlord insurance policies.
- Depreciation: The cost of the property (excluding land) spread over its useful life.
c. Depreciation and Capital Gains Tax
Depreciation allows landlords to recover the cost of the property over time. However, when you sell the property, you may be subject to capital gains tax on the profit. The tax rate depends on how long you’ve owned the property and your income level.
Recent Changes in Tax Laws
Tax laws are constantly evolving, and it’s important to stay updated on the latest changes that may affect your tax liability. Here are some recent updates related to rent payments and receipts:
- Increased Standard Deduction: The standard deduction has increased, which may affect the decision to itemize deductions.
- Changes in Depreciation Rules: Recent changes in depreciation rules may impact how landlords can depreciate their rental property.
- New Tax Credits: New tax credits may be available for energy-efficient improvements to rental properties.
Understanding how rent payments and receipts affect your tax liability is essential for both tenants and landlords. By staying informed about the latest tax laws and maintaining accurate records, you can ensure compliance and potentially reduce your tax burden. Whether you’re a tenant looking to deduct part of your rent for business use or a landlord seeking to maximize your deductions, this guide provides the information you need to navigate the complexities of rent-related tax laws.
-

Why AMD’s 8- and 12-core Ryzen AI processors are perfect for industrial edge AI robots
-

Oil prices, shipping chaos, security risks: Decoding Trump’s ‘mutual’ pact with Netanyahu on Iran
-

Why India Is Holding Petrol and Diesel Prices Steady Even as Brent Crude Crosses $102 — And How Long Can It Last?
-
Crude Oil Price Crisis 2026: $100/Barrel Nightmare – How It’s Crushing Global Markets & Your Wallet
With over 15 years of experience in Banking, investment banking, personal finance, or financial planning, Dkush has a knack for breaking down complex financial concepts into actionable, easy-to-understand advice. A MBA finance and a lifelong learner, Dkush is committed to helping readers achieve financial independence through smart budgeting, investing, and wealth-building strategies, Follow Dailyfinancial.in for practical tips and a roadmap to financial success!